The Revenue Blog /
Key Principles of Capacity Planning in Sales and RevOps
Key Principles of Capacity Planning in Sales and RevOps

Topics covered in this article
This article is a summary of the Sales Capacity Planning course from the RevOps Masterclass program. You can enroll today for free!
One of the most important cornerstones of sales planning is the prior determination of capacities. When planning for the next financial year, the sales manager should not only calculate the team size and potential fluctuations, but also consider individual experience and past performance as they become key prediction factors.
Defining Sales Capacity Planning and its Significance
Sales capacity planning is a critical process in the realm of revenue operations, serving as a strategic approach to determine if an organization possesses adequate resources, particularly in terms of personnel, to meet its planned targets.
It is a method of assessing whether the right amount of resources are in the pipeline and staffed to achieve annual objectives. This process is inherently complex and often takes several weeks to months.
A sales capacity model is important because it immediately shows whether the necessary resources are available to achieve the targets. In this context, resources go beyond sales staff and also include support functions in the areas of operations, enablement, sales consulting, and technology. This comprehensive involvement makes the process extensive and vital.
In addition, capacity planning helps management to set or adjust targets based on practical possibilities. It provides insight into the existing gap between current sales opportunities and the required pipeline generation, which impacts both inbound and outbound strategies.
Capacity models are crucial not only for setting targets but also for aligning with departments such as HR and finance to ensure the company has adequate staffing levels to achieve its goals. Ultimately, the success of sales capacity planning is critical in ensuring sales representatives can effectively meet their targets, which underlines its fundamental role in strategic sales management.
The Complexities and Timelines of Sales Capacity Planning
The capacity planning process is characterized by its complexity and varying duration, depending on the size and structure of the organization. As a rule, this planning phase can extend over several weeks or even months. It is often strategically placed in the third and fourth quarters of the year to prepare for the coming year’s goals and activities.
This timing is critical as it allows for comprehensive analysis and adjustments based on the current year's data and trends. While the process can be time-consuming, its complexity is justified by the need for detailed and accurate planning that ensures resources are optimally aligned with the organization’s goals and targets for the following year.
Key Principles of Effective Sales Capacity Planning
Effective capacity planning depends on several principles, each of which makes an important contribution to the success of the process. These principles are essential components for any organization seeking to optimize its capacity planning strategy.
Know the Average Sales Cycle Speed Across Segments
This principle emphasizes understanding how long it takes to bring a deal from initiation to close. It is important to differentiate this metric within various segments such as enterprise, mid-market, and small and medium-sized businesses. The speed of the sales cycle is a critical factor in capacity planning as it directly influences the timeframe for revenue realization. If this aspect is misjudged, it can lead to inaccurate forecasts and ineffective resource allocation.
Distinguish Tenured and Ramping Sales Reps
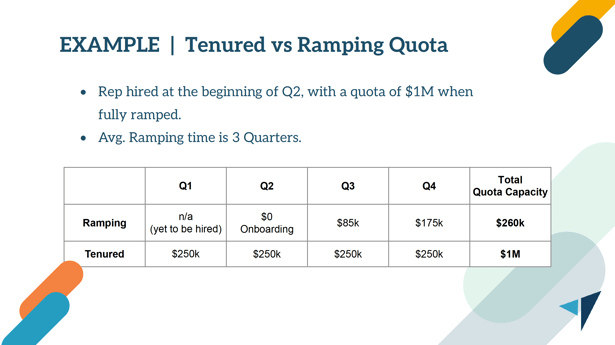
Accurately assessing the performance of tenured sales representatives versus those still ramping up is critical. This principle recognizes that new employees or those in the process of ramping up will not immediately contribute to the revenue targets at the same level as their more experienced counterparts. Ignoring this difference can lead to significant discrepancies in revenue projections and targets.
Rate Your Reps' Abilities
This principle is about assessing the performance of sales reps. It's not about labeling reps as good or bad, but understanding the differences in their ability to meet quotas. This nuanced approach requires close collaboration with sales managers to identify performance levels and create an accurate and realistic sales capacity planning model.
Hiring Dates are Important
Hiring dates play a critical role in capacity planning. The timing of new hires has a major impact on the company's ability to meet its sales targets. A delayed hiring process can lead to missed opportunities and gaps in the sales pipeline. This principle is closely linked to the HR and finance departments and underscores the need for synchronized planning and execution across departments.
Understand Current Pipeline Amounts and its Implications
This principle focuses on the existing pipeline and its potential contribution to revenue targets. This includes a thorough analysis of the pipeline, including early-stage deals and their expected size. This analysis helps to understand how much new business needs to be generated and what resources are required to achieve the targets, thereby resulting in effective sales forecasting. It's about matching the potential of the pipeline with the actual capacity of the sales team.
3 PRO Tips for Mastering Zero Dollar Amount Opportunities
- Early Engagement Analysis - Proactively assess early-stage pipeline opportunities. Implement a system to classify these prospects based on potential value, ensuring none slip through the cracks.
- Market-Specific Estimations - Tailor your deal size estimates by market segment. Utilize historical data and market insights to forecast potential deal values accurately, adapting your strategy to different customer profiles.
- Automate for Efficiency - Embrace CRM automation for assigning provisional values to opportunities. This not only streamlines your pipeline management but also provides a real-time, dynamic view of your capacity planning, making your sales process more responsive and data-driven.
Incorporating these principles into capacity planning provides a more holistic and accurate approach. This allows companies to effectively align their resources with their sales goals, taking into account the different dynamics of sales cycles, team compositions, and market conditions.
Practical Steps for Implementing Capacity Planning
How to calculate capacity? Effective implementation of capacity planning involves several practical steps that organizations can take to ensure a robust and workable strategy. These steps act as a roadmap for businesses looking to optimize their capacity planning process.
Build an Ad-hoc Capacity Model
The introduction of an ad-hoc capacity model is a crucial first step in capacity planning, especially for those who are new to the process or at the beginning of a financial year. While this model is not comprehensive, it serves as a preliminary assessment tool to evaluate the current status and development of an organization's capacity planning. It provides immediate, fundamental insights that allow for quick adjustments and strategic planning. This model can be created with available data, resources, and sales capacity planning software, and serves as a starting point for more detailed planning.
Collaborate Across Departments
Effective capacity forecasting and planning requires collaboration between the various departments of an organization. This includes open discussions with executives from sales, finance, HR, and other relevant departments to ensure a unified approach. This collaboration ensures that all aspects of capacity planning, from resource allocation to target setting, are coherent and aligned with the company's overall goals. These discussions help to identify gaps in understanding or expectations and promote a culture of transparency and shared responsibility.
Set Up a Review and Feedback Processof the Sales Capacity Model
Once the initial stages of capacity forecasting and planning have been completed, it is important to establish a review and feedback process. This involves regularly assessing the effectiveness of the capacity planning model and making the necessary adjustments based on feedback from key stakeholders. This iterative process ensures that sales capacity planning remains dynamic and responsive to changing business requirements and market conditions. It also enables continuous improvement by using insights from different departments to refine and improve the capacity planning strategy.
Common Mistakes in Capacity Planning and Sales Capacity Models
- Misjudging sales cycle lengths - A common oversight is underestimating the variability of the length of sales cycles in different market segments. This not only distorts sales forecasts but also disrupts resource allocation, leading to either a shortage of resources or a surplus in critical areas.
- Overlooking new rep ramp-up time - It is often wrongly expected that newly hired employees will immediately contribute to sales targets. This overlooks the important ramp-up time required for them to reach full productivity, leading to inflated and unrealistic revenue expectations.
- Inaccurate resource allocation - Aligning resources with sales targets is more art than science. The challenge is to match planned resources with actual requirements and ensure that each area is adequately staffed and equipped to achieve its goals.
- Misestimating pipeline contributions - Early-stage deals in the pipeline are often miscalculated, leading to either overestimation or underestimation of their potential. Accurate valuation at this stage is crucial for realistic forecasting capacity.
- Ignoring external market factors - External changes such as market trends or global events such as pandemics have a significant impact on sales performance. Failing to factor these into capacity planning can result in strategies that are out of sync with market realities.
- Misalignment with HR and finance departments - Coordination of plans with HR and finance departments is critical. Discrepancies in hiring plans, budgets, and sales targets can lead to strategic misalignments and affect the overall efficiency of capacity planning.
- Overgeneralizing sales data - Applying a 'one-size-fits-all' approach to diverse sales teams and markets is a recipe for error. It's critical to recognize individual and team performance variances, tailoring strategies to each unique market and team dynamic.
Conclusion
As we wrap up our exploration of capacity planning, let's turn our focus to your business. How can you apply the insights gained from this article to your business?
- Have you implemented capacity planning in your business? If not, what challenges have prevented you from starting this important process?
- Are you collaborating effectively across departments? Consider how aligning with finance, HR, and other teams can enhance your capacity planning efforts.
- Are you using historical data? Reflect on how historical sales cycles and performance data can inform your capacity planning model.
- What steps can you take right now? Take a moment to identify immediate actions you can implement, such as building an ad-hoc capacity model or encouraging cross-departmental collaboration.
Capacity planning isn't a one-size-fits-all solution, but a dynamic process that is tailored to the individual needs of your organization. By asking yourself these questions and applying the knowledge you gain, you can set yourself on the path to more effective resource allocation and strategic growth.
Interested in checking out the complete course?
Dive into further details of sales capacity planning here -> https://masterclass.boostup.ai/course/capacity-planning
BoostUp's RevOps Masterclass offers free courses from industry leaders that cover all aspects of RevOps while blending insights and actionable strategies. Sign Up for RevOps Masterclass Now->
FAQ - Sales Capacity Planning
What is sales capacity planning and why is it important?
Sales capacity planning is the process of determining if you have the right amount of resources, particularly sales reps and support roles, to achieve your annual targets. It's crucial because it quickly indicates whether the necessary resources are available to achieve these goals. This often complex and time-consuming planning is usually done in Q3 and Q4 for the following year, but ad hoc modeling can provide a quicker assessment.
What is a sales capacity model?
A sales capacity model is a structured framework that helps organizations assess if they have adequate resources, especially in sales and support roles, to meet revenue targets. The model considers several factors:
- Team size and structure,
- Individual performance metrics,
- Pipeline projections and current capacity needs.
What are the key principles for effective sales capacity planning?
Key principles include knowing the average velocity of the sales cycle and tailoring it to different team segments (such as enterprise or SME), differentiating between permanent and new hires, correctly assessing the skills of reps, recognizing the importance of the hire date, and considering the current state of the pipeline. These principles help to create accurate capacity forecasts and adjust strategies accordingly.
How can tools help with capacity planning in sales?
RO&I platforms can help with capacity planning by providing data and reporting capabilities to assess current status and trends. They can help create ad hoc models, track the performance of different team segments, and facilitate collaboration between departments. Tools streamline the process and make it more efficient and data-driven.
How can I start sales capacity planning in my organization?
To start sales capacity planning, follow these steps:
- Build an Ad-Hoc Capacity Model: Use current data to assess resource status and needs.
- Collaborate Across Departments: Involve sales, HR, and finance for unified input.
- Set a Review Process: Regularly adjust the model based on feedback and evolving market conditions.
How can I refine my sales capacity model?
Work with analysts to gather data and with managers to discuss the variables relevant to your team. Make sure the sales, finance, and HR departments are aligned on goals and hiring plans. Review your model regularly, be open to feedback, and make the necessary adjustments to continuously improve it. Remember that capacity planning is a dynamic process that evolves with the needs of your business.
How does capacity planning impact sales forecasting?
Capacity planning enhances sales forecasting by providing insights into resource effectiveness. It impacts forecasting by:
- Improving Accuracy: Aligns forecasting with real capacity, avoiding overly optimistic projections.
- Resource Optimization: Helps allocate resources based on actual demand and sales cycle insights.
- Cross-Functional Input: Uses data from multiple departments (sales, finance, HR) to create a well-rounded forecast.
About the Author
Matt DurazzaniMatt Durazzani is the Chief Revenue Officer at Olumo and has over two decades of revenue operations and growth expertise.



-Photoroom.png)