The Revenue Blog /
Sales Forecasting - How to Predict Revenue - Examples & KPIs
Sales Forecasting - How to Predict Revenue - Examples & KPIs

Batu Apaydin
January 25, 2024
18 min read
Topics covered in this article
Sales forecasting is about predicting future sales performance and giving companies valuable insights into their revenue generation path. By effectively forecasting sales, businesses can make informed decisions that drive growth, optimize the use of resources, and achieve their strategic goals.
Ambitious but realistic plans are in the interest of the whole company. It's not just the sales department that needs to know how much revenue is planned for the next financial year, and who-what-when to contribute to make it happen.
Do you wonder “How do I forecast sales?” Our comprehensive guide dives into the details, providing a thorough understanding of the sales forecasting definition, sales forecasting methods, and practical sales forecasting examples. It also highlights the role of sales forecasting software and templates in streamlining the process and improving accuracy. Our comprehensive guide is designed to help newcomers and experienced sales experts alike forecast and plan for success.
What is a Sales Forecast?
What Sales Forecasting Means for Your Business
What is sales forecasting? Think of it as your company’s GPS, guiding you through the ever-changing market landscape. It's about predicting your future sales over a specific period – such as a quarter or a year – based on a comprehensive analysis of past trends, market conditions, and customer behavior.
It’s not just about numbers, but about giving you a clear idea of where your business is heading. With a well-developed sales forecast, not only can you guess what you want to do next, but you can also plan it strategically. This makes your financial planning more solid and aligns your business strategies with real outcomes.
Sales Forecasting vs. Demand Planning: Knowing the Difference
Have you ever wondered how sales forecasting differs from demand planning? Although they may seem similar at first glance, they play a very specific role in the success of your business. Sales forecasting focuses on predicting your sales and provides important insights for financial and strategic decisions. It’s about determining what you can realistically sell based on hard data and market knowledge.
Demand planning, on the other hand, takes a broader scope. It’s about understanding overall market demand and aligning your inventory, production, and resources with that demand. It’s a collaborative endeavor, with teams from sales to finance working together to ensure your business runs like a well-oiled machine.
The Positive Impact of Sales Forecasting on Your Business
Why is sales forecasting so important for your business? Quite simply, it’s your roadmap for growth and stability. A solid sales forecast empowers you to make informed strategic decisions, from new product launches to market expansion. It’s about making the right bets.
By allocating your resources wisely, you avoid unnecessary spending and focus on the areas with the greatest growth potential. If you set realistic targets based on your sales forecast, you'll always be on track to achieve your goals and ensure the financial health of your business.
The sales forecast is also your early warning system. It helps you identify potential challenges before they become major problems, so you can act quickly and keep your business on track. In short, sales forecasting isn’t just a part of your business strategy, it’s a catalyst for your success, alerting you to opportunities and keeping you away from pitfalls. It’s not just about surviving in a competitive market, it’s about succeeding.
Key Components and Data Sources for Accurate Sales Forecasting
Essential Metrics for Forecast Accuracy
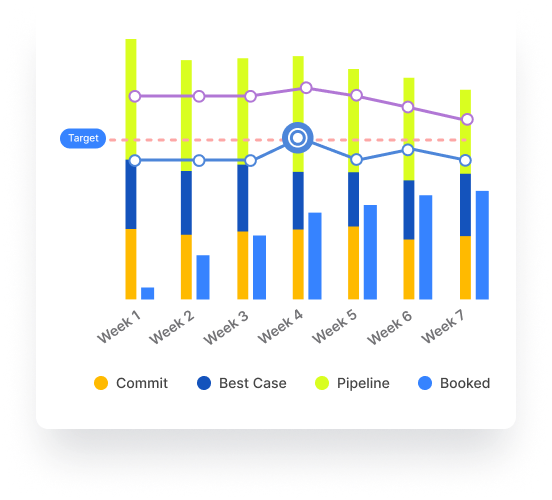
Accurate sales forecasting depends on effectively tracking key metrics. These metrics give you a clear overview of your sales performance and forecast health:
- Weekly and Quarterly Target Tracking. Monitoring progress against set targets during these periods will help identify performance trends and areas that need attention.
- Historical Forecast Accuracy. Reviewing how accurate past forecasts were compared to actual sales outcomes offers insights for future forecasting.
- Pipeline Coverage Assessment. Analyzing coverage gaps in your current and upcoming quarters' pipeline to predict end-quarter performance.
- Conversion Rate Analysis. Historical data is used to determine the conversion rate in the pipeline, which provides insight into the volume each sales rep needs to achieve their targets.
Leveraging AI for Enhanced Forecasting
Artificial Intelligence (AI) brings a new level of sophistication to sales forecasting. By integrating data from various sources such as CRM and ERP systems, AI algorithms can detect patterns that would be invisible to human analysts. For example, AI's ability to analyze point-of-sale data in real-time allows it to connect sales trends with external factors such as market fluctuations, leading to more accurate forecasts.
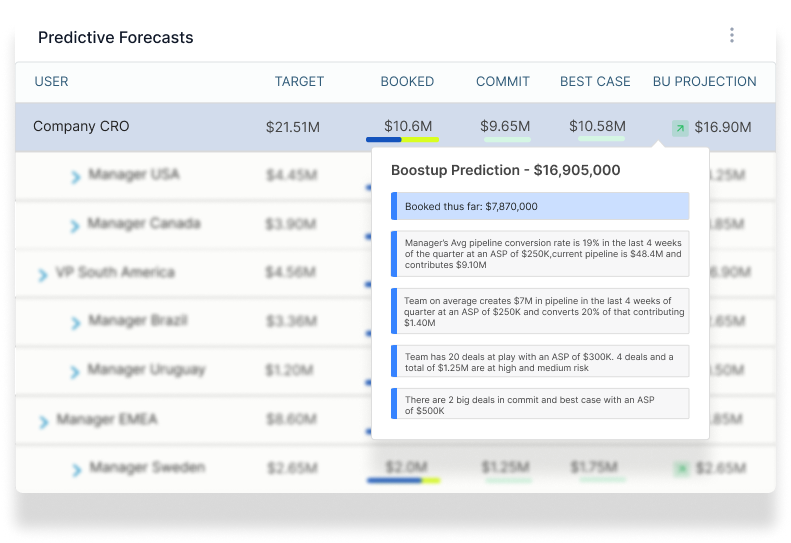
AI's strength lies in its capacity to process large data sets quickly and accurately. When it comes to sales forecasting, this means AI can provide insights into customer preferences, buying patterns, and the length of sales cycles. The result is a comprehensive analysis that forms the basis of a highly accurate sales forecast, often achieving precision levels up to 95%.
When used strategically, these components not only improve the accuracy of your forecasts but also provide actionable insights for informed decision-making and effective strategic planning in your business.
Step-by-Step Guide to Sales Forecasting
If you ever asked “How to do a sales forecast”, read on as we discuss the necessary steps that you can follow.
Setting the Foundation: Objectives and Time Frame
Start your sales forecasting by clearly defining your goals. What do you want to achieve? Is it to determine potential revenue, allocate a budget, or set sales targets? Your goals will guide the forecasting process. Next, you need to decide on a timeframe. Are you going to look at the next quarter, the next year, or some other period? This time frame will determine how you collect and analyze data.
Data Collection and Organization
Data is the cornerstone of forecasting. Collect comprehensive data from CRM systems, records of customer contacts such as emails or calls, market research, and macroeconomic trends. Focus on automated data collection to minimize errors and ensure efficiency. Organize this data systematically, as it forms the basis for your forecasting.
Selecting the Right Forecasting Method
The choice of sales forecasting method depends on your specific business context. For established products with historical data, quantitative methods such as time series analysis are effective. This method examines past sales to identify trends and patterns, which is useful in various scenarios such as retail or e-commerce demand forecasting. For new markets or products, on the other hand, qualitative approaches based on expert knowledge may be more suitable.
Using Advanced Techniques
Incorporate advanced machine learning techniques such as Random Forest and Gradient Boosting to gain deeper insights. These methods can handle complex data relationships better than traditional linear models and help with strategic decision-making. They are particularly useful for tasks such as strategic product placement and market entry strategies.
Practical Application
Apply your chosen forecasting method in practice. Evaluate past sales trends and adjust them to anticipated changes in pricing, customer base, promotions, and market conditions. It is important that you take market trends, competitor activity, and your business plans into account when you forecast.
Consider using sales forecasting software or tools that can automate parts of this process, especially for data analysis and applying complex statistical models.
Integrating Multiple Forecasting Approaches
Often, combining different forecasting methods yields the best results. These can include historical data, funnel-based forecasting, and complex models that take lead scoring and macroeconomic influences into account. Approaches such as regression-based analysis or lead scoring for sales forecasting can add depth to your forecasts.
Continuous Monitoring and Adaptation
Remember, sales forecasting is not a one-off task. It requires ongoing monitoring and adaptation. Regularly compare your forecasts against actual sales, and be ready to adjust your approach as market conditions change. Feedback from various departments can also provide valuable insights for refining your forecasting process.
By following these steps methodically and choosing appropriate methods, you can create a dynamic and effective sales forecasting process that aligns with your business strategy and supports informed decision-making.
Combined and AI-Driven Forecasting
Sales forecasting involves predicting future sales to help businesses make informed decisions regarding resource allocation, budgeting, and business strategy development. The two primary categories of sales forecasting methods are qualitative and quantitative, each with its unique approach and application. In addition to the combination of these methods, AI is used for more accurate sales forecasting.
Qualitative Methods
Qualitative forecasting methods are less about crunching numbers and more about using the insights of experienced people inside or outside the organization. These methods are particularly useful in situations where quantitative data is scarce or not entirely reliable.
Quantitative Methods
Quantitative forecasting methods use historical data and mathematical models to predict future sales. These data-driven approaches are most effective when a large amount of reliable data is available.
The Rise of Predictive Sales Forecasting
Predictive sales forecasting represents a significant leap in the way businesses approach their sales strategies. By leveraging data, machine learning algorithms, and AI, predictive forecasting can analyze past and current sales data to make accurate sales forecast predictions about future sales trends. This approach goes beyond traditional forecasting methods by not only looking at historical data but also incorporating various external factors such as market dynamics, changing consumer behavior, and even socio-economic trends.
Harnessing Machine Learning and AI
The core of predictive forecasting lies in the use of advanced machine learning and AI technologies. These technologies can process vast amounts of data at incredible speeds, identifying patterns and correlations that might be invisible to the human eye.
For example, AI can analyze years of sales data in conjunction with current market trends to forecast future sales with a high degree of accuracy. Thanks to this ability, businesses can better anticipate market changes and adapt their strategies accordingly.
Benefits of AI-Driven Forecasting
AI-driven forecasting offers several key advantages:
- Improved Accuracy. AI algorithms can analyze complex data sets and predict sales outcomes with greater precision than traditional methods.
- Time Efficiency. These systems can process and analyze data much faster than manual methods, freeing up valuable time for sales teams to focus on strategy and customer engagement.
- Dynamic Adaptability. AI-driven forecasting can quickly adapt to changes in data or market conditions, providing businesses with up-to-date insights.
- Actionable Insights. Beyond just predicting sales, AI can offer actionable insights to optimize sales strategies, product positioning, and market expansion.
Sales Forecasting Use Cases and Examples by Industries
How to forecast sales in your industry? What are the best examples? Here are some use cases illustrating how sales forecasting can be effectively utilized:
1. Retail Sector
- Inventory Management. Retailers use sales forecasting to determine the amount of inventory needed to meet expected customer demand, especially for seasonal products.
- Promotional Planning. Forecasting helps in planning sales promotions, like discounts or special offers, by predicting periods of higher or lower demand.
- New Product Launches. Before introducing a new product, retailers forecast expected sales to determine production volumes and marketing strategies.
2. Manufacturing Industry
- Supply Chain Optimization. Manufacturers rely on sales forecasts to manage their supply chain, ensuring they have enough raw materials to meet production needs without overstocking.
- Capacity Planning. Sales forecast reports help the decisions on whether to scale up or down manufacturing operations, which directly impacts labor and production costs.
- Product Lifecycle Management. Forecasting helps in planning for the different phases of a product's lifecycle, from the ramp-up of production for a new product to the phase-out of an older product.
3. Technology and Software Companies
- Subscription Revenue Forecasting. For SaaS (Software as a Service) companies, forecasting is crucial to predict recurring revenue from subscriptions.
- Resource Allocation for Development. Sales forecasting helps to prioritize resources for product development and focus on features or products with higher expected demand.
- Market Penetration Strategies. For new software products or updates, forecasts help in strategizing market entry and penetration tactics.
4. Service Industry
- Staffing and Resource Management. Service-oriented businesses like consulting firms or agencies use sales forecasts to manage staffing levels, ensuring they have sufficient capacity to meet client demands.
- Service Expansion Decisions. Forecasts help in determining when to introduce new services or expand into new markets.
- Revenue Management. Particularly in industries like hospitality, forecasting is key in managing pricing strategies to maximize revenue.
5. Financial Services
- Revenue Predictions for Investment. Sales forecasts provide financial analysts and investors with important information for assessing a company's future sales potential and making well-founded investment decisions.
- Risk Assessment. When assessing credit risk, lenders consider a company’s sales forecast as part of its overall financial health.
6. Healthcare and Pharmaceuticals
- Demand Forecasting for Medications. Pharmaceutical companies forecast sales to ensure sufficient production of medicines, especially those with a limited shelf life.
- Resource Allocation in Healthcare Facilities. Hospitals and clinics forecast patient numbers to effectively allocate resources such as staff, beds, and medical equipment.
7. E-commerce Platforms
- Optimizing Online Inventory. E-commerce companies create sales forecasts to effectively manage their stock levels, avoid overstocking, and ensure product availability at the same time.
- Targeted Marketing Campaigns. Sales forecasting helps with the planning and implementation of targeted marketing campaigns during peak shopping periods.
8. Automotive Industry
- Production Planning. Car manufacturers create sales forecasts to plan production volumes and align them with expected market demand.
- Dealership Inventory Management. Sales forecasting helps dealers manage their vehicle inventory and ensure a balance between variety and overstocking.
Sales Forecasting Best Practices and Challenges
Navigating Common Forecasting Challenges
While sales forecasting is important, it also comes with challenges that can affect its accuracy and usefulness:
- Accuracy and Trust Issues. When companies rely on tools such as spreadsheets for their forecasting, they often struggle with accuracy, leading to distrust of the forecasts.
- Subjectivity in Forecasting. It's a delicate balance between using judgment and relying on credible forecasting methods. Too much emphasis on judgment can lead to subjective forecasts.
- Usability Across Departments. A forecast must be useful to multiple stakeholders. If it's not tailored to the needs of different teams, its effectiveness is significantly reduced.
- Inefficiency in the Forecasting Process. Inefficiencies arise when there are no clear responsibilities or standardized rules in the forecasting process, leading to disputes and confusion.
- Wrong Insights from Sales Data. Often, sales data doesn't accurately reflect the status of deals, mainly due to over-optimistic reporting by sales reps.
- Time-Consuming Manual Processes. Manual forecasting processes aren't only time-consuming but also take valuable time away from actual sales activities.
Best Practices for Effective Forecasting
To overcome these challenges, several best practices can be applied:
- Integrate Findings into Business Processes. Ensure that forecasting insights are integrated into broader business processes for maximum impact.
- Cross-Departmental Involvement. Involve various departments in the forecasting process to gain a more comprehensive view.
- Regular Communication. Keep all stakeholders, including sales and marketing teams, in the loop about forecasting findings.
- Leverage Technology. Use technology to capture data, analyze, and automate processes to increase efficiency and accuracy. Use sales forecasting software to manage a large pipeline of opportunities.
- Regular Revisits and Adaptation. Review and adjust forecasts regularly, especially in response to market changes.
- Comprehensive Data Analysis. Include all relevant historical, economic, and market trends in the forecast analysis.
- Encourage Collaboration and Communication. Foster a culture of collaboration and open communication between different departments.
- Overcome Resistance to Change. Resolve resistance to new forecasting methods and encourage the adoption of more effective practices.
- Data Collection and Analysis Accuracy. Ensure the accuracy of data collection and analysis to avoid skewed forecasts.
By understanding these challenges and implementing these best practices, businesses can enhance the accuracy and reliability of their sales forecasting. This leads to more informed decisions and a more solid strategy for managing market dynamics.
Conclusion
How to do sales forecasting? As we wrap up this comprehensive guide on sales forecasting, we invite you to think about how you can apply the lessons learned to your business. Consider what steps you can take to improve the accuracy of sales forecasts and how you can utilize new technologies and methods to stay ahead of the curve in predicting future sales.
Remember that your contribution and actions today will determine the success of your forecasts tomorrow. How will you implement these strategies in your business? Share your thoughts and plans on how you will integrate sales forecasting into your business strategy. Your journey to more accurate and effective sales forecasting starts here.